Digital video advertising is changing faster than we can keep up with.
The name of the game is always going to be delivering the perfect ad to the perfect customer at the perfect time. But how is that accomplished in a world where cookies are being phased out and consumers are becoming more weary of online privacy, all while still demanding relevant ads?
The answer is contextual targeting.
What is contextual targeting?
Contextual targeting is a method of determining ad placement by matching the ad with contextually relevant content.
Intent is signaled at the video level, which improves accuracy when it comes to ad placement.
Imagine you’re looking to place a 15-second video ad for a coffee company. You can use contextual targeting to find video content that’s directly or indirectly relevant to coffee consumption based on what’s actually occurring at that moment in the video.
By placing your video within contextually relevant content, you’re nearly doubling your chances of brand recall and purchase intent.
What are the benefits of contextual targeting?
1. It preserves privacy
As third-party cookies are being phased out, advertising will need to make the necessary adjustments to ensure targeting is more effective than ever.
By relying on video signals rather than behavioral signals, ad relevancy is determined at the content-level, rather than at the user level. Users concerned with privacy will feel much more comfortable knowing that they’re still seeing relevant ads without invasive tactics that compromise their online security.
2. The ads are more relevant
Depending on the ad, there’s no better way to reach the right customer at the right time with the right ad than with contextual targeting. By analyzing what’s occurring in the video at that moment, you’re reaching a customer at their peak engagement.
Ad personalization is still a priority for consumers. Contextual targeting ensures that users are still seeing ads that mean something to them without relying on third-party data or sneaky opt-in clauses.
3. It overcomes the deficiencies of negative keywords
Negative keywords are less relevant in the contextual advertising world. That’s because contextual targeting bypasses the parameters set at the keyword level by uncovering deeper signals that better translate to ad relevancy.
AI and machine learning is evolving to the point of understanding user sentiment without the assistance of negative keywords. This helps in determining the best placement of your ads. But, more importantly, it determines where not to place your ads.
For example, if you’re looking to place an ad for a new plant-based food item, you might be tempted to use negative keywords to steer away from content that focuses heavily on animal consumption, such as sites that sell barbecues.
But what if one of those sites that sells barbecues has a popular video about best ways to grill vegetables? By relying on negative keywords, you’d be excluding a highly relevant ad based on poorly executed sentiment analysis.
Contextual targeting would look beyond the keywords and actually decipher the vegetables on the screen, which is where you would want your ad to show up.
4. Improved return on ad spend (ROAS)
Contextual advertising spend is expected to double by 2030.
Ad buyers are doubling down on contextual’s efficacy because it can potentially deliver much higher ROAS than behavior targeting.
Next to product placement, contextual targeting is the most seamless way to incorporate your ad within the content being consumed. The difference is that you don’t need to pay a studio or content creator for people to see your ad.
In fact, the contextual advantages in video are 93% boost in ad recall and purchase intent when compared to behavioral targeting.
Without having to rely on harvesting third-party data which can be enormously expensive, contextual targeting circumvents inferential or even incomplete data set at the URL level.
This means spending less on acquiring customer data and reallocating critical budget towards premium video that is much more aligned with your user’s habits and viewing trends.
5. Scales through multiple content verticals
Instead of surrendering to the confines of vertical-specific page classification, a video-first contextual strategy opens up a world of inventory—upwards of 70% more reach when decoupling video and page level categorization.
Think of a sneaker brand that wants their video ad to run on online videos about jogging. The advertiser has previously been limited to setting up individual deals with endemic niche jogging sites. However, there are hundreds of untapped jogging videos on music sites (e.g., “Spring 2021 Workout Playlist”), on news sites (e.g., “Benefits of Jogging on Heart Health”), on lifestyle sites (e.g., “Spring Athleisure Trends”).
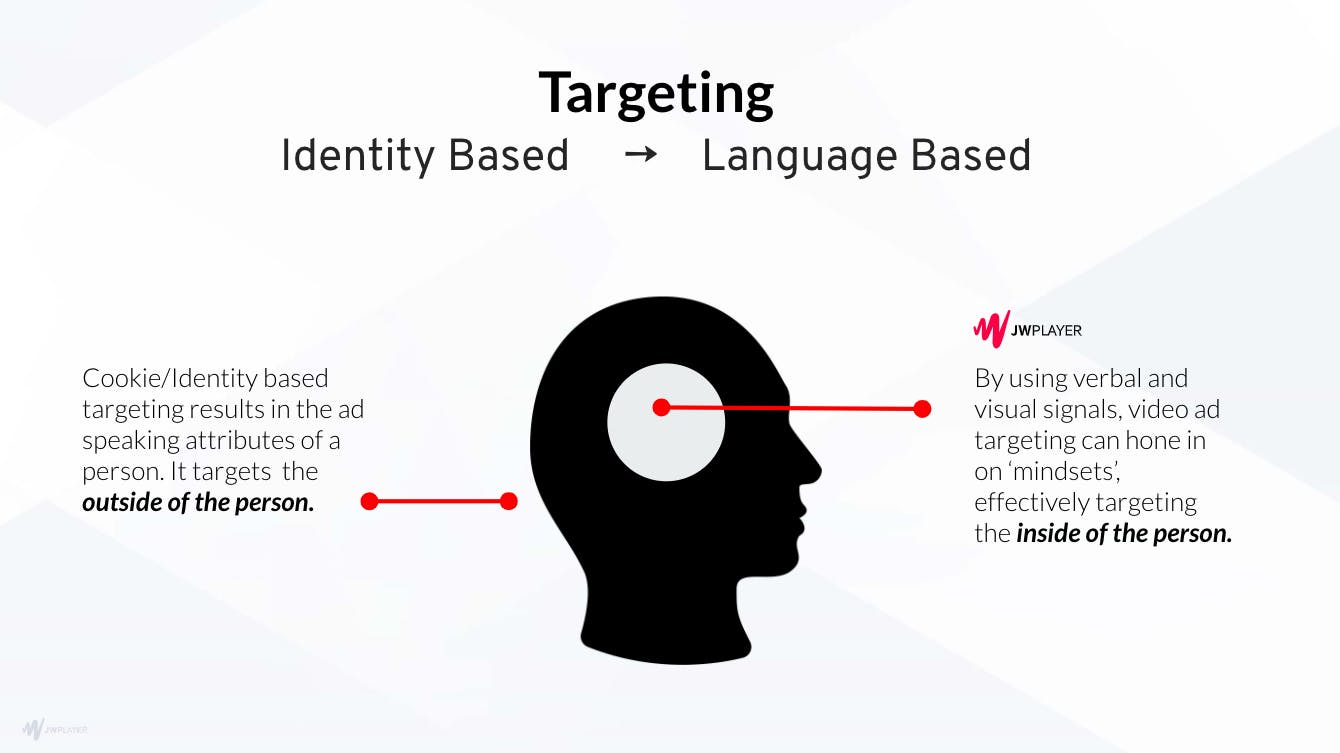
Advertisers now have the ability to target the video content completely independently of the website classification. The result is more accurate alignment, and a world of incremental reach.
See how you can maximize your ad yield and deliver the perfect ad to the perfect audience at just the right time with JWP.
